asdfasdfasdf
TL;DR
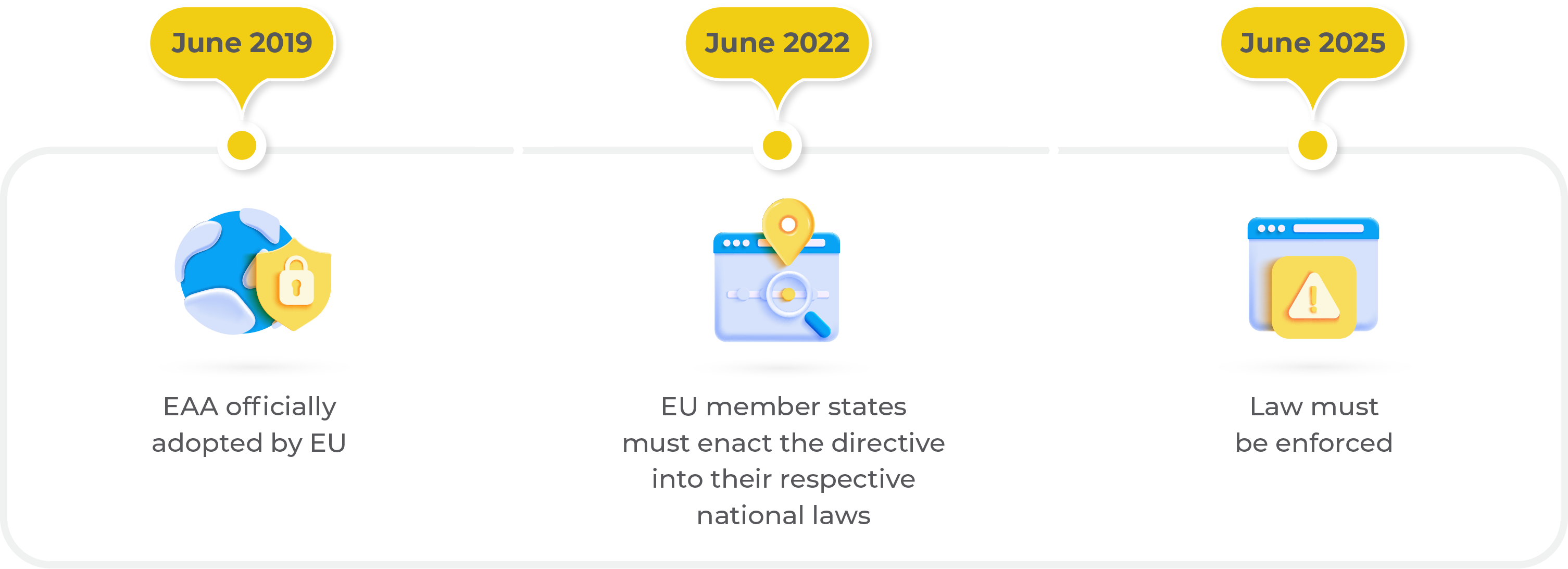
The EAA comes into effect June 28, 2025 for businesses providing products or services to customers in the EU.
- The law seeks to make it easier for businesses to scale accessible products and services by unifying divergent laws across member countries
- Not only will companies avoid penalties by complying with EAA, providing accessible content is also better for your brand
- Websites and digital content must comply with EN 301 549 v3.2.1, which is based on WCAG 2.1 AA.
- Digital content must be perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust
- A combination of automated and manual validation will be required to check for compliance
What is the EAA?
The European Accessibility Act (EAA) is a European Union directive coming into effect on June 28, 2025. Its goal is to make products and services more accessible to individuals with disabilities. The Act aims to harmonize varying accessibility laws across EU member states so that it’s easier for companies to scale accessible solutions.
Why Does it Matter?
Businesses that serve residents in the EU must comply with a specific checklist of inclusive web experience standards. Building accessible digital products is the right thing to do.
Failure to comply could result in:
- Fines (to be defined by individual EU member states)
- Lawsuits
- Costly operational resources as you seek to address non-compliance
What Products and Services Are Covered?
The law specifies that websites and digital content must comply with the below requirements and called out these particular modalities of products and services to pay special attention to the performance criteria:
- E-commerce
- Banking services
- Transportation
- Telecommunications
- Audio-visual media
- Computer hardware and operating systems
- TV hardware and broadcasting services
- ATMs and self-service kiosks
- Smartphones and mobile applications
- Ticketing & check-in machines
- Ebooks and digital content
Website & Content Requirements:
- Content must be consistently and adequately accessible for users’ perception, operation, and understanding
- Websites should provide Interoperability with user agents and assistive tech
- Content presentation and interaction must include adaptability
- Fonts should be adequate in size and shape, have sufficient contrast, and offer adjustable spacing between letters, lines, and paragraphs
- Provide text formats that can be used to generate alternative assistive formats
- Alternative formats for non-textual content
- Statement providing information on how the company’s products or services meet accessibility requirements
Exemptions
The following types of website content are exempt:
- Pre-recorded media published before June 28, 2025
- Office files published before June 28, 2025
- Online maps (as long as essential info is accessible if intended for navigation)
- Third-party content not controlled, developed, or funded by your organization
- Archived web/app content not updated after June 28, 2025
The EAA also aims to avoid disproportionate burdens on smaller entities such as individual professionals, small to medium-sized enterprises (SME), and microenterprises. Member countries are encouraged to set light rules that are proportionate for SME costs and capabilities, while microenterprises are exempt.
Business Size Definitions:
- Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs): <250 employees and/or < €43M annual balance sheet
- Microenterprises: <10 employees and/or < €2M annual balance sheet (exempt from EAA) to Accessibility, lawmakers have been busy worldwide, enacting safer privacy laws to protect
How is Accessibility Defined?
Accessibility under the EAA is based on EN 301 549 v3.2.1, which aligns with:
- WCAG 2.1 AA guidelines (Potential future upgrade to WCAG 2.2)
- Supplemental standards for interface design, PDFs, biometrics, content management systems
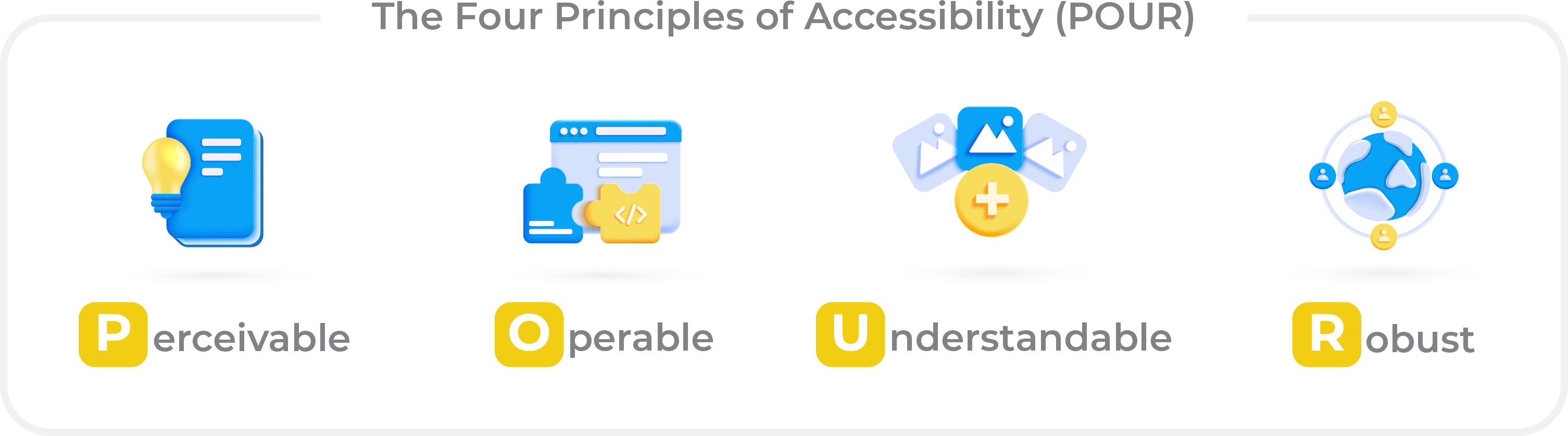
POUR Principles:
- Perceivable: Users must be able to perceive information and interfaces
- Operable: Navigation must be user-friendly
- Understandable: Information and operation interfaces must be clear and understandable
- Robust: Content must be robust enough to be interpreted by assistive tools
Functional Performance Criteria Include:
- Vision impairments (none, limited, color-blindness)
- Hearing impairments (none, limited)
- Vocal limitations
- Motor skill limitations
- Seizure triggers
- Cognitive, learning, and language disabilities
Are Accessibility Overlays or Widgets Enough?
No. Accessibility overlays (JavaScript widgets, AI-driven fixes) do not ensure compliance.
Why Not?
According to the European Commission:
The European Disability Forum and International Association of Accessibility Professionals have warned that overlays can interfere with assistive tech and may track sensitive user data.
How ObservePoint Can Help
ObservePoint supports the first step of accessibility compliance: auditing your website for accessibility.
What It Does:
- Provides automated, continuous detection of WCAG compliance issues at scale
- Does not fix accessibility issues but helps identify and pinpoint them
Effective Accessibility Compliance Requires:
- Continuous detection with a combination of automated and manual processes
- Ongoing manual remediation
To find out more about how ObservePoint monitors websites for accessibility, read the following help docs:
- What parts of WCAG ObservePoint monitors
- Recommended manual checks (e.g., color contrast, dynamic content, contextual clarity of text, voice recognition)
Summary
Preparing for the EAA means taking a proactive, comprehensive approach to accessibility.
Automated audits like those from ObservePoint can assist, but full compliance requires a combination of ongoing automated and manual effort.
Compliance Deadline: June 28, 2025
Key Takeaway: Begin your accessibility audit now to stay ahead of regulatory risk and build a more inclusive digital experience.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered legal advice.